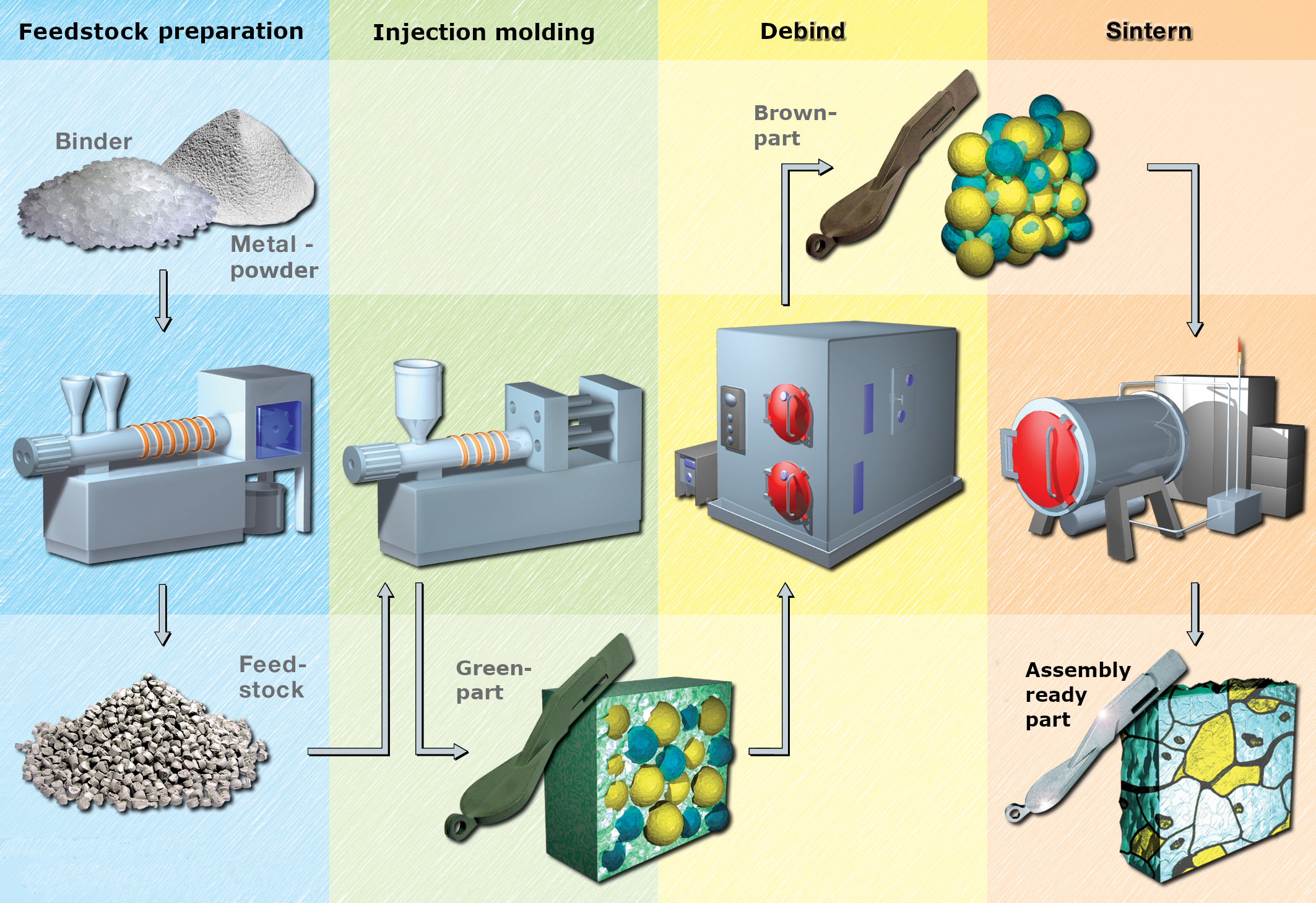
With this technology, the advantages of plastic injection molding (geometric design freedom) are combined with the advantages that are known from powder metallurgy (processing of demanding, difficult or non-machinable, possibly also non-castable construction and functional materials).This makes it possible to mass-produce complex, ready-to-install molded parts made of metal with maximum reproducibility and a wide range of material properties.
Green part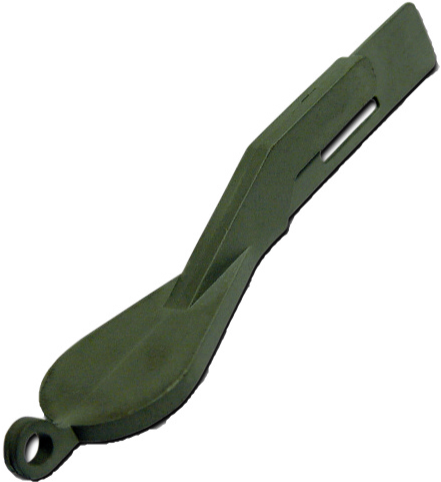 | Brown part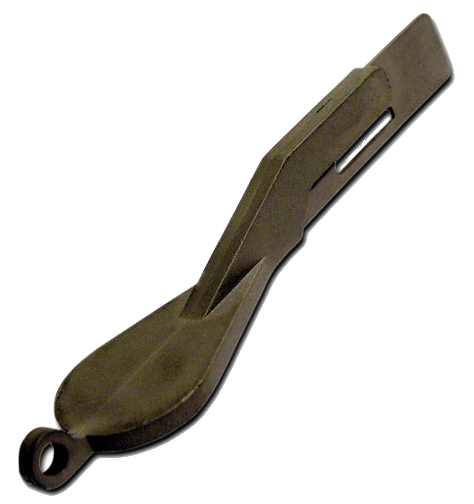 | Sinter part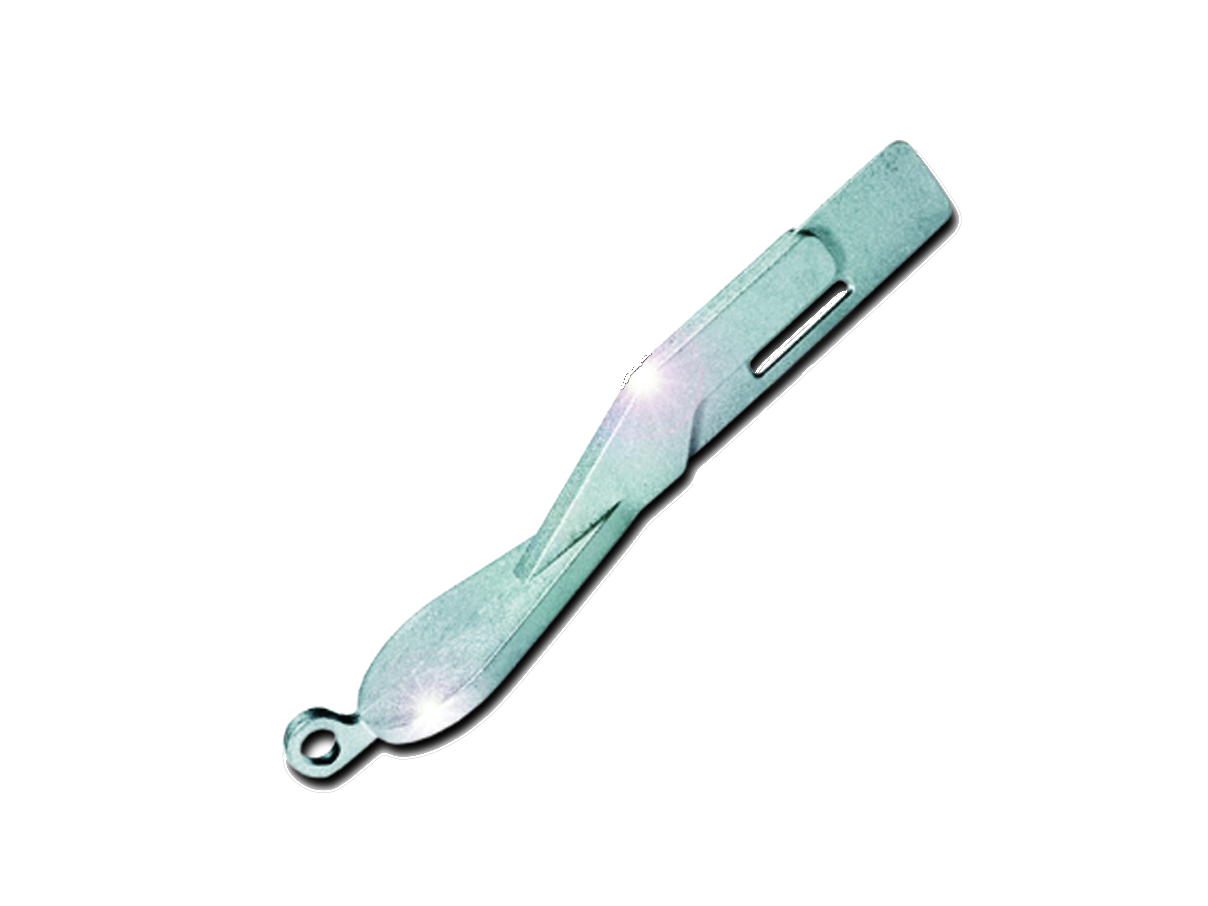 |
|---|---|---|
| Injection-molded part with a binder content of approx. 10 percent by weight. |
By removing the first binder component,
the so-called matrix, the still unsintered, porous brown part. |
Completely debindered and solidified by sintering component, which is dimensionally tightly tolerated and ready for installation. |
|
Properties: - high density of 97%, - homogeneous powder distribution, - no alignment of the powder particles. |
Properties: - Compliance with tight tolerances, - Density of 97% of the theoretical density, - round, separated, evenly distributed micropores, - no crack formation due to micropores. |
|
| These properties lead to non-directional shrinkage and a high component density, which is a prerequisite for gas-tight sintered parts. |